
- #Cellprofiler analysing a set of images for mac os x#
- #Cellprofiler analysing a set of images software#
- #Cellprofiler analysing a set of images plus#
- #Cellprofiler analysing a set of images free#
ilastik provides realtime feedback that enables the user to interactively refine the segmentation result and hence further fine-tune the classifier.
#Cellprofiler analysing a set of images plus#
ilastik supports up to three spatial plus one spectral dimension and makes use of all dimensions in the feature calculation. A random forest classifier is used in the learning step, in which each pixel's neighborhood is characterized by a set of generic (nonlinear) features. Based on these labels, ilastik infers a problem specific segmentation. ilastik learns from labels provided by the user through a convenient mouse interface. We propose ilastik as an easy-to-use tool which allows the user without expertise in image processing to perform segmentation and classification in a unified way. The analysis of biological high content images often requires segmentation as a first step. The Review particularly highlights the insights from single-cell data from both sequencing technologies and in situ imaging of tissues.read more read lessĪbstract: Segmentation is the process of partitioning digital images into meaningful regions. This article discusses methods - primarily computational tools - for characterizing diverse aspects of cancer–immune cell interactions, including antigen presentation, T cell repertoires and heterogeneity in cell types and cell states.
The interactions between tumours and the immune system are highly complex. Here, we review computational tools for interrogating cancer immunity, discuss advantages and limitations of the various methods and provide guidelines to assist in method selection.
#Cellprofiler analysing a set of images software#
In order to process, analyse and visualize multidimensional data sets generated by these technologies, computational methods and software tools are required. In parallel, numerous novel cutting-edge technologies for comprehensive molecular and cellular characterization of cancer immunity have been developed, including single-cell sequencing, mass cytometry and multiplexed spatial cellular phenotyping. This study documents the extent, origins and consequences of genetic variation within cell lines, and provides a framework for researchers to measure such variation in efforts to support maximally reproducible cancer research.read more read lessĪbstract: The remarkable success of cancer therapies with immune checkpoint blockers is revolutionizing oncology and has sparked intensive basic and translational research into the mechanisms of cancer–immune cell interactions. When the 27 MCF7 strains were tested against 321 anti-cancer compounds, we uncovered considerably different drug responses: at least 75% of compounds that strongly inhibited some strains were completely inactive in others. Analyses of single-cell-derived clones demonstrated that continuous instability quickly translates into heterogeneity of the cell line. Barcoding experiments showed that cell line evolution occurs as a result of positive clonal selection that is highly sensitive to culture conditions. Notably, genetic changes were associated with differential activation of gene expression programs and marked differences in cell morphology and proliferation. Similar results were obtained with multiple strains of 13 additional cell lines. Further comprehensive genomic characterization of 27 strains of the common breast cancer cell line MCF7 uncovered rapid genetic diversification. Here we use genomic analyses of 106 human cell lines grown in two laboratories to show extensive clonal diversity. Although cell lines are known to evolve in culture, the extent of the resultant genetic and transcriptional heterogeneity and its functional consequences remain understudied. We implemented an automatic build process that supports nightly updates and regular release cycles for the software.Ĭontact: information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.read more read lessĪbstract: Human cancer cell lines are the workhorse of cancer research.
#Cellprofiler analysing a set of images for mac os x#
It is available as a packaged application for Mac OS X and Microsoft Windows and can be compiled for Linux.

#Cellprofiler analysing a set of images free#
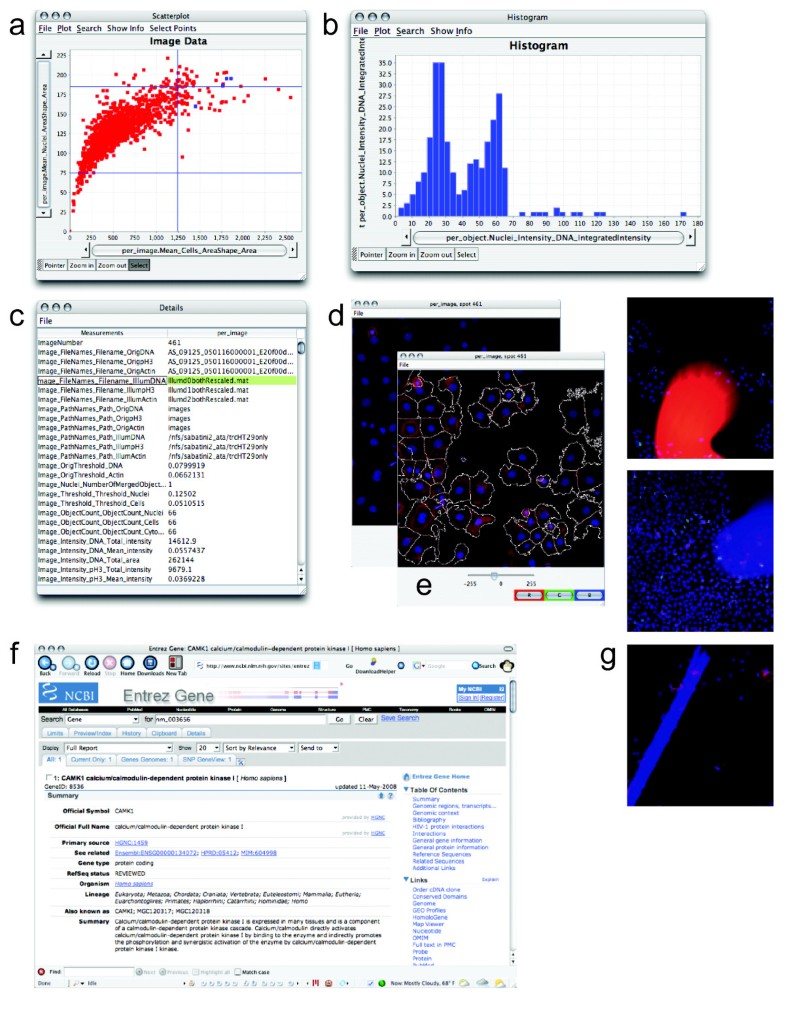
CellProfiler Analyst 2.0, completely rewritten in Python, builds on these features and adds enhanced supervised machine learning capabilities (Classifier), as well as visualization tools to overview an experiment (Plate Viewer and Image Gallery).Īvailability and Implementation: CellProfiler Analyst 2.0 is free and open source, available at and from GitHub () under the BSD license. Abstract: Summary: CellProfiler Analyst allows the exploration and visualization of image-based data, together with the classification of complex biological phenotypes, via an interactive user interface designed for biologists and data scientists.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
